
Banks, credit unions, and financial institutions lend capital to individuals, families, and businesses. A clear takeaway from credit risk management is driving profits by knowing the A-Z’s of borrower profiles. However, here are a few best practices for credit management that’ll help your business stand apart. Or do you want to go beyond the requirements and improve your business with your credit risk models?
How to incorporate trend analysis into your credit risk assessment process?

With expected loss quantified, lenders turn to a structured assessment process that applies these insights across every borrower. By integrating and quantifying these diverse factors, lenders can fine‑tune scorecards to reflect each borrower’s true risk profile. Lenders must also monitor loans closely to ensure they get paid on time and in full. This includes regular contact with the borrower and, if necessary, taking action to recover past-due payments. In this article, we’ll define credit risk, give some examples, explain the main types of credit risk, and provide detailed insight into how lenders calculate credit risk before extending credit.
- As part of the ‘three lines of defence’ model, the Risk division is thesecond line of defence providing oversight and independentchallenge to key risk decisions taken by business management.
- Basel I, introduced in 1988, marked the moment when credit risk became a formally defined regulatory category.
- AI can detect early warning signs, predict defaults, and recommend personalized credit limits.
- This recognition led to the emergence of the first international prudential coordination efforts, culminating in the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision.
- Credit risk measures how likely a borrower is to pay back a loan—whether it’s a mortgage, a personal loan or a credit card.
Overcoming Data Gaps

Lenders use credit risk to evaluate whether a borrower is a reliable investment. The higher the credit risk, the higher the interest rate lenders typically charge to offset the risk of losing money on the loan. In the context of insurance, lenders can also purchase various types of insurance to reduce their financial exposure in the market.
- When financial institutions extend credit, they take on the risk that the borrower may not fully repay the debt.
- A borrower with substantial capital is seen as less risky because they have additional financial buffers.
- Investors use strategies like investment diversification to invest in a wide array of debt investments, such as corporate bonds, U.S.
- For a closer look at our rigorous journalistic standards, explore our editorial guidelines.
- With C&R Software’s FitLogic rules engine, you gain a cost-effective solution that turns potential weak spots into competitive advantages, ensuring your institution’s financial efficiency and sustainable growth.
- His client-centric approach and deep understanding of market trends have made him a trusted advisor to a diverse clientele.
Ramp: Your partner in credit risk management
With end-to-end platforms, our account and portfolio management services can help you limit risk, detect fraud, automate underwriting and identify opportunities to grow your business. Experian is a leading provider of traditional credit data, alternative credit data and credit risk analytics. Advances in analytics, computing power and real-time access to additional data sources are helping lenders better measure some of the C’s. Investors use strategies like investment diversification to invest in a wide array of debt investments, such credit risk definition as corporate bonds, U.S.
- Despite the challenges, adopting best practices, leveraging advanced technology, and maintaining a proactive approach to risk management ensures that organisations can mitigate risks effectively.
- The credit acceptance criteria must take into consideration common creditcharacteristics for distinct categories of counterparties or facilities, and theboundaries of the credit risk strategy and credit risk policy.
- But, at the end of the day, none of the methods provide absolute results—lenders have to make judgment calls.
- In simple terms, banks experience credit risk when assets in a bank’s portfolio (borrowed loans) are threatened by loan defaults.
- In this article, we’ll define credit risk, give some examples, explain the main types of credit risk, and provide detailed insight into how lenders calculate credit risk before extending credit.
Regulatory frameworks for credit risk
- To assess this risk, most lenders take into consideration things like a borrower’s credit scores, DTI ratio and total debt.
- The Group operates a number of solutions to assist borrowers whoare experiencing financial stress.
- By applying them appropriately, financial institutions can enhance their credit quality and profitability while reducing their credit losses and risks.
- In other words, it is the possibility that a borrower may default on a loan or fail to make payments as per the agreed terms.
- If it borrows during a boom period, the bank must also consider its performance during any subsequent depression.
- Credit risk is the probability that a borrower will fail to repay their debts.
Defaults can occur due to economic distress, job loss, or business failures, affecting loan repayments. Lenders use your credit history to help assess your “character” as part of credit risk analysis. They look to your past habits to guess how you’ll manage debt in the future. As you use your credit card or loans, your financial institution typically reports your credit activity to the three credit bureaus. If your credit report shows a pattern of missed payments or several new credit card accounts in a short period, lenders may consider you a high-risk borrower.

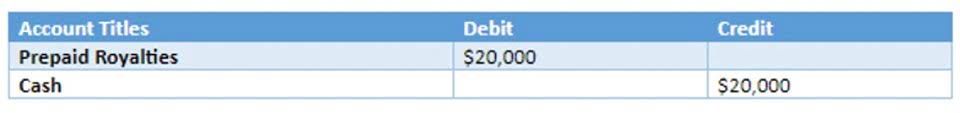
Mitigation reduces the Accounting Errors loss-given default (LGD), which is the percentage of exposure that will not be recovered in the event of default. Credit rating also helps banks determine the loss-given default (LGD) of a borrower or a debt instrument, which is the percentage of exposure that will not be recovered in the event of default. Credit ratings can be done internally by the bank’s credit analysts or externally by independent rating agencies.
Real-time risk monitoring
Credit risk is a term used to describe the potential financial loss a lender may experience when a borrower fails to repay a loan or credit. Automated workflows make processes standard and reduce human error to speed up decisions. Character https://www.bookstime.com/ looks at intentional default, capacity checks financial ability, and collateral shows what can be recovered if things go wrong. Cash flow statements need extra attention because they show real money movement, not just accounting profits. Strong operating cash flows that stay steady show better chances of surviving economic downturns. These days, banks and lenders tend to use a mix of statistical models and business rules.
0 Comments